SMB Service Screen
5 minute read.
The System > Services screen includes three options on the SMB service row:
- View Logs opens the Audit screen.
- View Sessions opens the SMB Status screen.
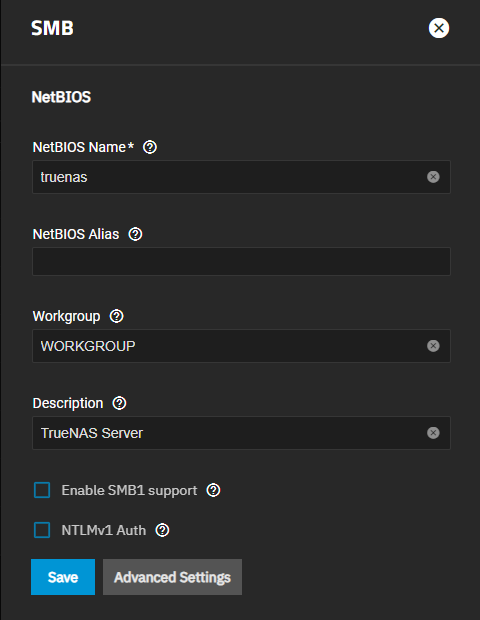
- Configure icon opens the SMB Service screen showing the Basic Settings by default.
The SMB service screen displays setting options to configure TrueNAS SMB service settings to fit your use case.
Click Save or Cancel to close the configuration screen and return to the Services screen.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| NetBIOS Name | Enter the NetBIOS name for the TrueNAS system (maximum 15 characters). Cannot contain: `\ / : * ? " < > |
| NetBIOS Alias | Enter alias names (maximum 15 characters each). Cannot contain: `\ / : * ? " < > |
| Workgroup | Enter a name that matches the Windows workgroup name (maximum 15 characters). Cannot contain: `\ / : * ? " < > |
| Description | (Optional) Enter any notes or descriptive details about the service configuration. |
| Enable SMB1 support | Select to allow legacy SMB1 clients to connect to the server (see caution below). SMB audit logging does not work when using SMB1. |
| NTLMv1 Auth | Off by default. Select to allow smbd attempts to authenticate users with the insecure and vulnerable NTLMv1 encryption. This setting allows backward compatibility with older versions of Windows, but we do not recommend it. Do not use on untrusted networks. |
As of TrueNAS 22.12 (Bluefin) and later, TrueNAS does not support SMB client operating systems that are labeled by their vendor as End of Life or End of Support. This means MS-DOS (including Windows 98) clients, among others, cannot connect to TrueNAS SMB servers.
The upstream Samba project that TrueNAS uses for SMB features notes in the 4.11 release that the SMB1 protocol is deprecated and warns portions of the protocol might be further removed in future releases. Administrators should work to phase out any clients using the SMB1 protocol from their environments.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
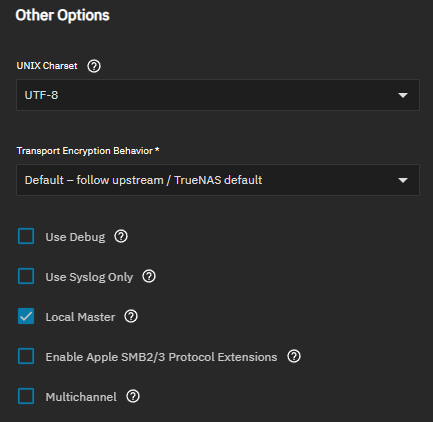
| UNIX Charset | Select the character set to use internally from the dropdown list of options. UTF-8 is standard for most systems as it supports all characters in all languages. |
| Transport Encryption Behavior | Select the option for the level of transport encryption to implement. Options and behaviors:enable_smb1) |
| Use Debug | Select to log more detailed information about SMB. By default, TrueNAS logs error and warning-level messages. We do not recommend enabling debug logging for production servers as it can generate large log files and impact performance. |
| Use Syslog Only | Select to log authentication failures in |
| Local Master | Selected by default and determines if the system participates in a browser election. Leave cleared when the network contains an Active Directory or LDAP server or when Vista or Windows 7 machines are present. |
| Enable Apple SMB2/3 Protocol Extensions | Select to allow MacOS to use these protocol extensions to improve the performance and behavioral characteristics of SMB shares. TrueNAS requires Apple SMB2/3 protocol extensions for Time Machine support and Final Cut Pro Storage Share workflows. You must enable this setting before creating shares with the Time Machine Share or Final Cut Pro Storage Share purpose options. |
| Multichannel | SMB multichannel allows servers to use multiple network connections simultaneously by combining the bandwidth of several network interface cards (NICs) for better performance. SMB multichannel does not function if you combine NICs into a LAGG. |
| Enable Search (Spotlight) | Allows macOS clients to use Spotlight to search for file contents on SMB shares. Enables the TrueSearch indexing service, which indexes all enabled, non-encrypted SMB shares. Requires an Enterprise license or TrueNAS Connect configuration. When the setting is unavailable, a notice displays with a link to configure TrueNAS Connect. Encrypted datasets are not indexed. |
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
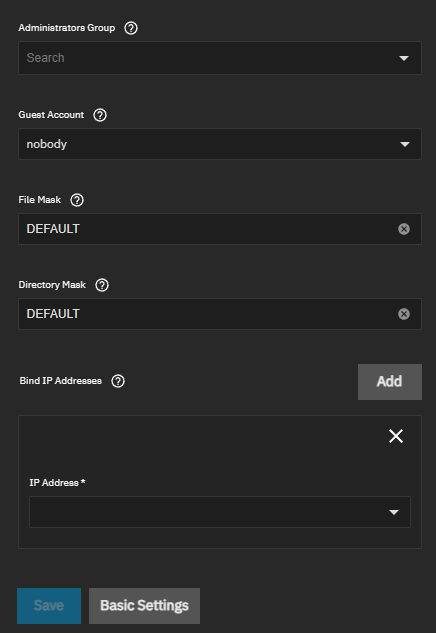
| Administrators Group | Enter or select members from the dropdown list. Members of this group are local administrators and automatically have privileges to take ownership of any file in an SMB share, reset permissions, and administer the SMB server through the Computer Management MMC snap-in. |
| Guest Account | Select the account for guest access from the dropdown list. The default is nobody. The selected account must have permission for the shared pool or dataset. To adjust permissions, edit the dataset Access Control List (ACL), add a new entry for the chosen guest account, and configure the permissions in that entry. If you delete the selected Guest Account, the field resets to nobody. |
| File Mask | Overrides default 0664 file creation mask, which creates files with read and write access for everybody. |
| Directory Mask | Overrides default directory creation mask of 0775, which grants everyone directory read, write, and execute access. |
| Bind IP Addresses | Click Add to specify static IP addresses that SMB listens on for connections. Select an IP address from the dropdown list for each entry. Leaving this empty defaults to listening on all active interfaces. |