Cloud Credentials Screens
10 minute read.
These providers are supported for Cloud Sync tasks in TrueNAS:
- Amazon S3
- Backblaze B2
- Box
- Dropbox
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Google Cloud Storage
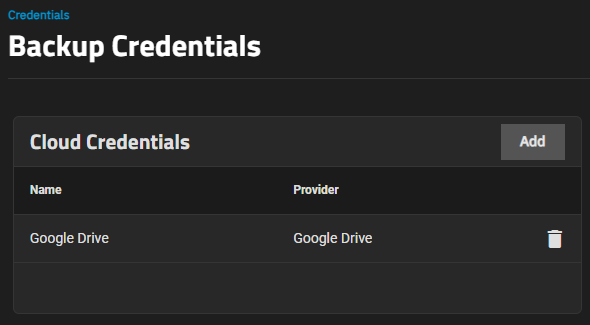
- Google Drive
- Google Photos
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Hubic (closed to new accounts)
- Microsoft Azure Blob Storage
- Microsoft OneDrive
- OpenStack Swift
- pCloud
- SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)
- Storj iX*
- WebDAV
- Yandex
*TrueCloud backup tasks streamline functionality for Storj iX cloud backups and restoration.
The Cloud Credentials widget displays a list of cloud storage credentials configured on the system.
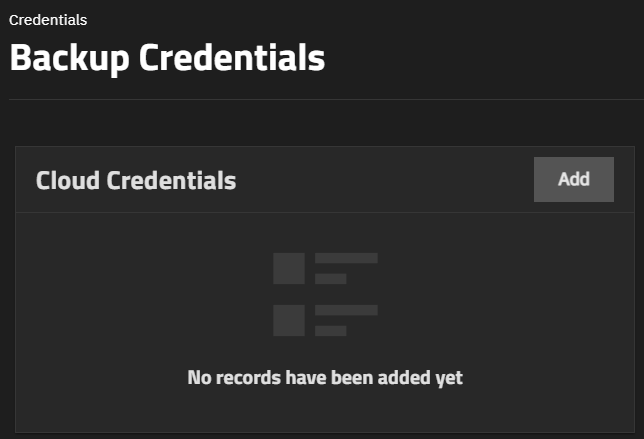
Before adding cloud credentials for a cloud storage provider, the Cloud Credentials widget displays No Cloud Credentials configured.
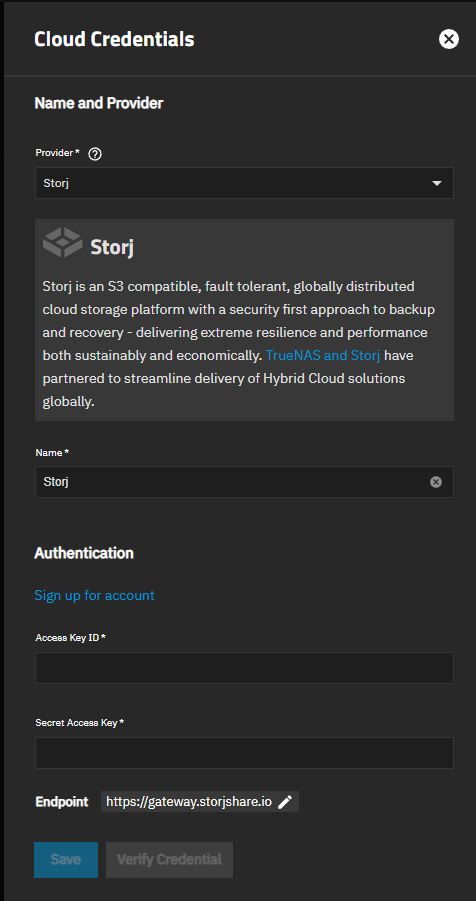
Add opens the Cloud Credentials configuration screen.
The Cloud Credentials configuration screen opens pre-populated with Storj-iX as the provider. It shows settings to add or edit cloud credentials TrueNAS uses to integrate with cloud storage providers.
Provider shows a list of available providers. Select the name of a cloud provider to populate the configuration screen with credential settings for that provider.
Verify Credentials uses the credentials entered to verify access to the cloud storage provider account.
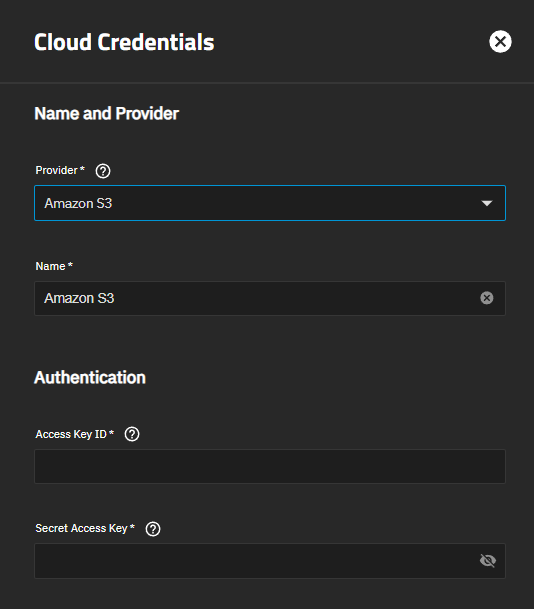
The selection in Provider changes the Authentication settings.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Provider | (Required) Default is set to Storj. Select the cloud storage provider from the options on the dropdown list. |
| Name | Enter a name for this cloud credential. For example, cloud1 or amazon1. |
Storj authentication includes going to the Storj iX sign-in screen to either create a new Storj iX account or log into an existing Storj iX account. After configuring the Storj account in the Storj-iX portal, return to TrueNAS to enter the S3 credentials provided by Storj.
Amazon S3 has basic authentication and advanced authentication settings. This section provides information on the basic authentication settings.
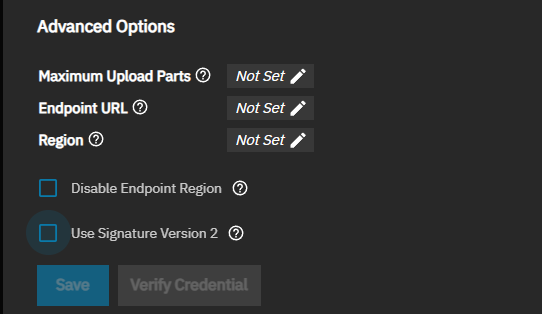
This section provides information on Amazon S3 advanced authentication settings for endpoints. The basic authentication settings are required when using the advanced settings.
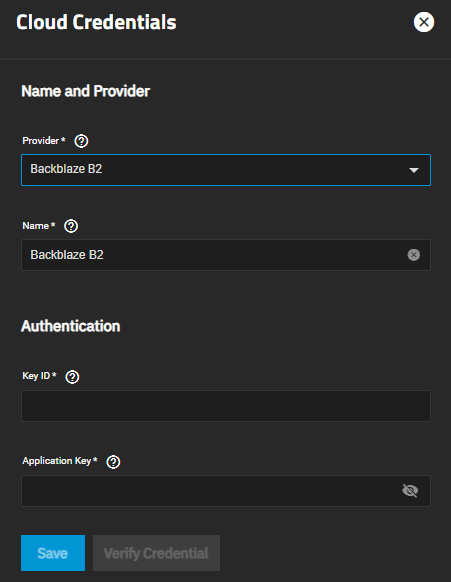
This section provides information on the BackBlaze B2 authentication settings.
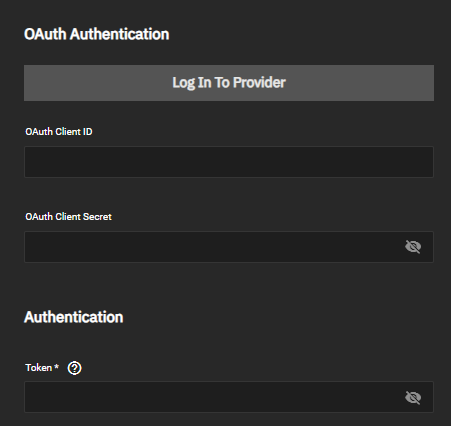
Several cloud storage providers use OAuth authentication and a required access token to authenticate the cloud storage account. Providers using these methods are Box, Dropbox, Google Photos, pCloud, and Yandex.
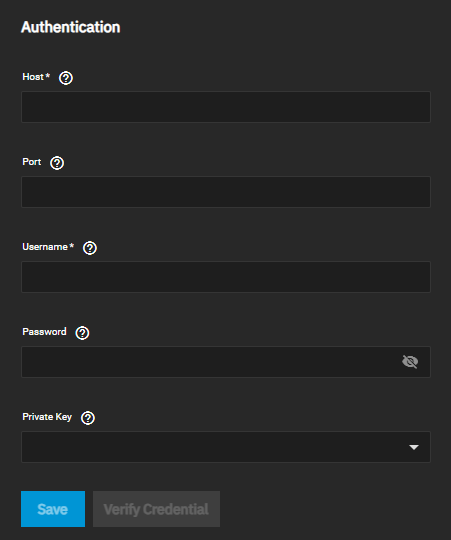
FTP and SFTP cloud storage providers use host name, port, and user credentials to authenticate accounts. SMTP uses SSH hosts, port, and user credentials and also uses a private key.
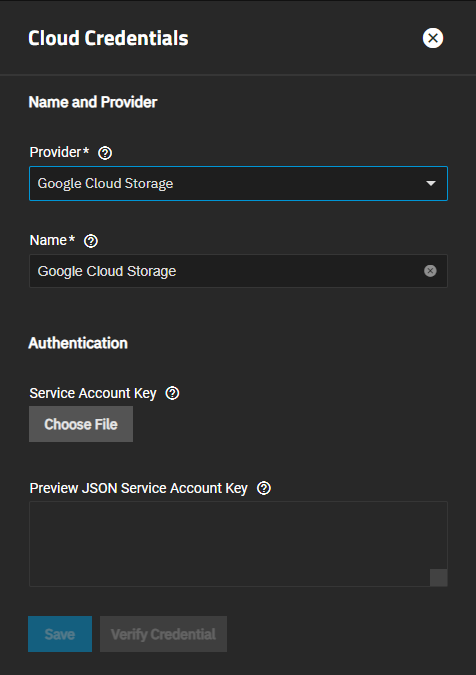
Google Cloud Storage authentication uses a Google service account JSON key credential file to authenticate the account.
Google Drive also uses OAuth authentication, a required access token, and a team drive ID to authenticate accounts. Google Drive adds one additional authentication setting to the general OAuth settings.
HTTP uses an HTTP host URL to authenticate account credentials. It is a read-only client that supports directory listings from popular web servers like Apache and Nginx.
Hubic uses an access token to authenticate the account. Enter the token generated by a Hubic account into the Access Token field.
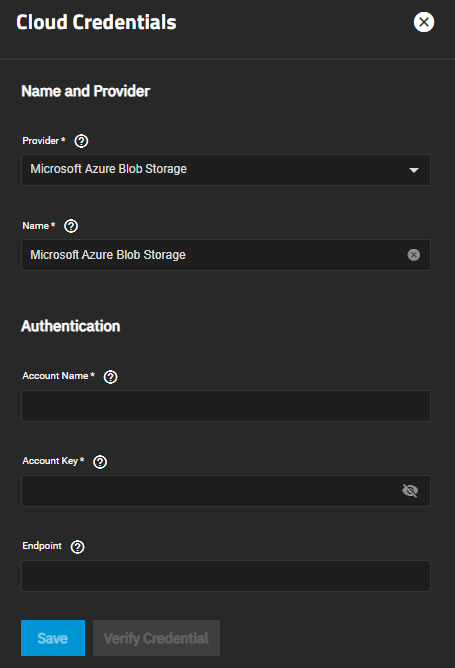
Microsoft Azure Blob Storage uses the Microsoft Azure account name and account key to authenticate the account credentials.
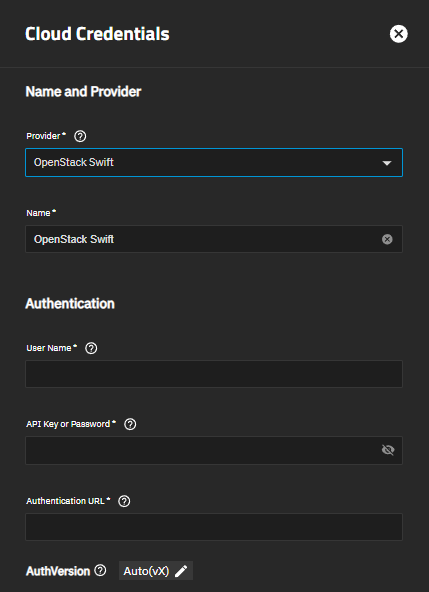
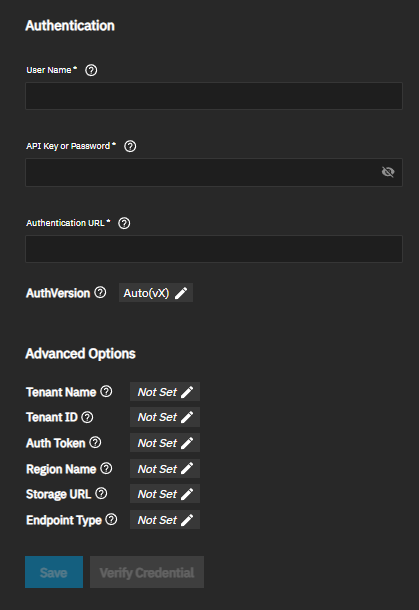
OpenStack Swift uses several required settings to authenticate credential accounts. The AuthVersion setting selection changes setting options displayed in Advanced Options.
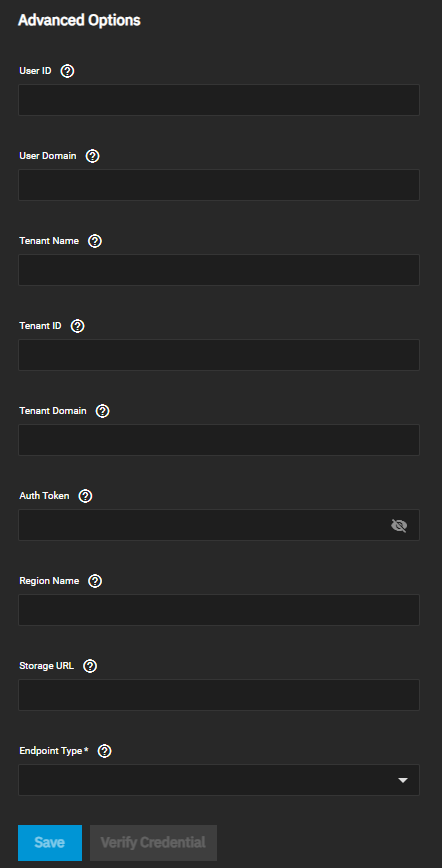
The Authentication Advanced Options screen shows different options based on the AuthVersion setting. Auto(vX), v1, and v2 use the same advanced authentication settings.
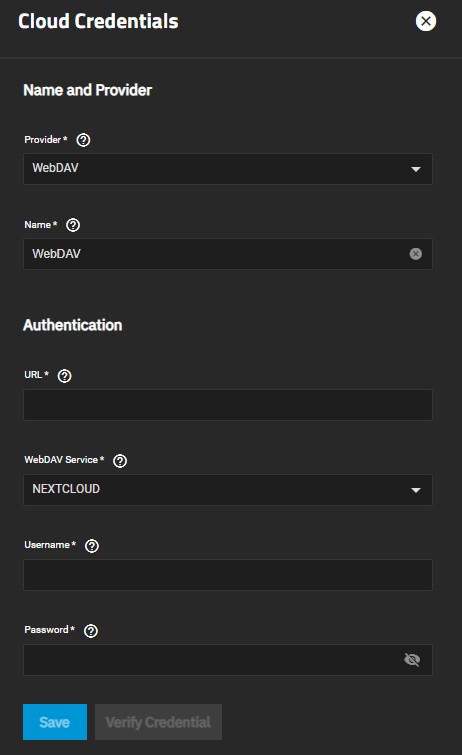
WebDAV uses a URL, service type, and user credentials to authenticate the cloud account credentials.
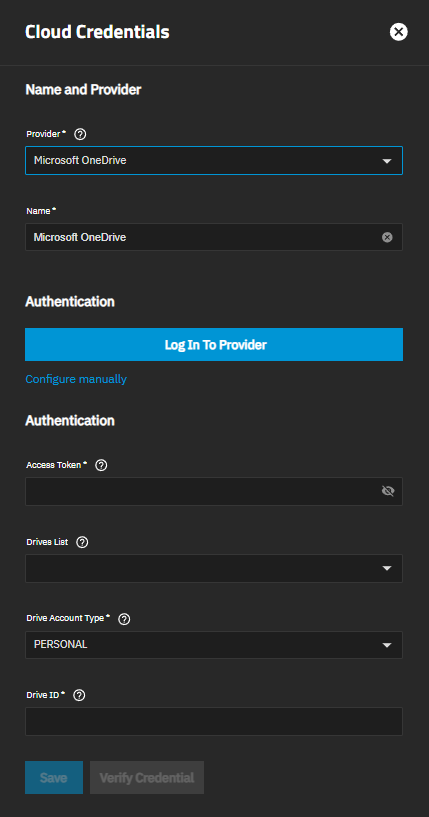
Microsoft OneDrive uses several required settings to authenticate credential accounts.