Setting Up a Remote Replication Task
13 minute read.
Remote replication backs up data stored on an originating TrueNAS system to a second remote destination TrueNAS system. TrueNAS allows scheduling a one-time or regularly scheduled ZFS snapshot of data stored in pools, datasets, or zvols, and saves them in another system.
With the implementation of the administration user and role-based permissions, setting up replication tasks as an admin user has a few differences from those set up when logged in as the root user. Setting up remote replication when logged in as the admin user requires selecting Use Sudo For ZFS Commands.
The first snapshot taken for a task creates a full file system snapshot, and all subsequent snapshots taken for that task are incremental to capture differences occurring between the full and subsequent incremental snapshots.
Scheduling options allow users to run replication tasks daily, weekly, monthly, or on a custom schedule. Users also have the option to run a scheduled job on demand.
Remote replication requires that the admin user on the remote system has SSH access, the SSH connection public key added, a home directory, and sudo command permission. The SSH service must be on when running the periodic snapshot and replication tasks. Setting options change based on the source and destination selections.
When setting up remote replication:
Set up the data storage for replicated snapshots. On the remote system, go to Datasets to add a dataset for the replicated data (snapshots).
TrueNAS does not allow you to create a new dataset using the Source or Destination file browsers in the replication wizard or the Add Replication Task configuration screen. After selecting the existing dataset where you want to store replicated data, the Destination file browser allows you to specify (create) a directory in an existing dataset on a local or remote system. You cannot create a directory for a dataset selected in the Source file browser.
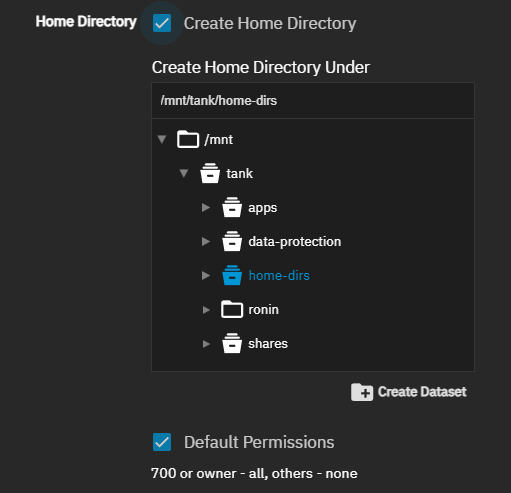
Add a home directory for the admin user on the local and the remote systems. The Home Directory path on the Add User or Edit User screen must be set to something other than /var/empty.
Click on the Home Directory setting to show the options.
Select Create Home Directory, then use the file browser to select an existing dataset or use Create Dataset after selecting the parent dataset to create a new dataset for home directories.
See Managing Users for more information on home directories, SSH access, and sudo commands.
Set up an SSH connection in TrueNAS before creating a remote replication task.
You can go to Credentials > Backup Credentials > SSH Connection and click Add to create an SSH connection, or select Generate New on the SSH Connection dropdown in the Replication Task Wizard to create an SSH connection to the remote system.
To configure an SSH connection, you need the IP address or host name for the remote system, and the administrator username and credentials. The administrator user on the remote system must have SSH access and the SSH service enabled so the local TrueNAS system can authenticate and communicate with the remote system.
You can configure the SSH connection while configuring the replication task, but using the Credentials > Backup Credentials > SSH Connection option to add a new connection between the local and remote system allows you to properly configure the administration user associated with the task before you add the replication task. If not properly configured, TrueNAS shows error messages stating the issue preventing you from continuing.
Using the Add SSH Connection screen creates the connection and keypair. You can obtain the public key from the keypair screen to copy/paste into the admin user on both the local and remote systems before you open the replication wizard.
Update the admin user settings to to allow SSH access, add the public key for the SSH credential for the remote system, and allow sudo commands.
Go to Credentials > Backup Credentials > SSH Credential. Add a new credential to the remote system if one does not exist, and then edit it to see the public key. Copy the public key to add to the admin user on the remote system. You can add the credential on the local or remote system.
On the remote system, go to Credentials > Users, select the admin user, and click Edit. Verify the account configuration has SSH Access selected. If not, select it, and then paste the public key for the SSH connection in the Public SSH Key field.
Click on Sudo Commands and select Allow all sudo commands with no password to enable it.
Save changes.
Check the SSH Service settings. Go to System > Services > SSH and click the edit icon. Select Allow Password Authentication to enable this function. Save the change.
Incorrect SSH service settings can impact the ability of the admin user to establish an SSH session during replication and require you to obtain and paste a public SSH key into the admin user settings.
Enable Start Automatically if you want the SSH service to start after a system restart, and then start or restart the service.
To configure the remote replication task, follow the instructions in the section below.
Use the Replication Task Wizard to create and copy ZFS snapshots to another system, which streamlines creating simple replication tasks. After creating the replication task, TrueNAS automatically creates a periodic snapshot task for sources that have no existing snapshots.
If you have an existing replication task, you can select it on the Load Previous Replication Task dropdown list. This loads the configuration settings for that task into the wizard, where you can make changes such as assigning it a different destination, setting a new schedule, or retention lifetime, etc. Saving changes to the configuration creates a new replication task without altering the task originally loaded into the wizard. This saves some time when creating multiple replication tasks between the same two systems.
Before you begin configuring the replication task, first verify that the destination dataset where you plan to store the replication snapshots is free of existing snapshots, or that snapshots with critical data are backed up before you create the task.
After completing the basic preparation steps in the section above, go to Data Protection > Replication and click Add to open the replication wizard. To configure advanced settings, click Advanced Replication Creation to open the Add Replication Task screen before you enter any settings in the wizard. Refer to the Advanced Replication Tasks for configuration instructions using the Add Replication Task screen.
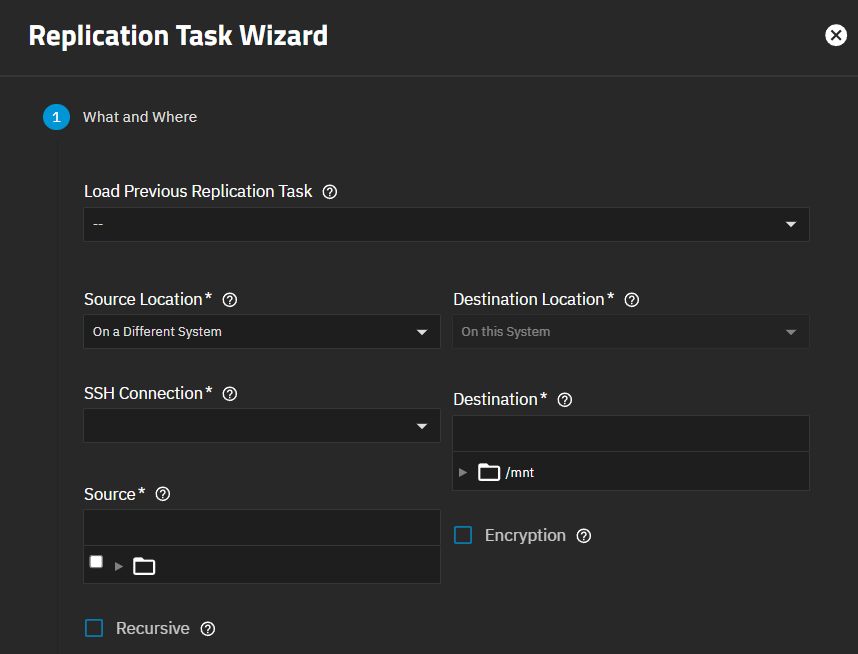
On the What and Where replication wizard screen:
Select an existing replication task from the Load Previous Replication Task dropdown. If one does not exist, leave this set to the default, which is the double dashes.
Select the source and destination locations. You can select these in any order. Local replication sends or receives data from one storage location to another on the same (local) system. Remote replication sends data to or receives data from a storage location on a different (remote) TruNAS system.
To set up a local replication in the replication wizard, set both Source Location and Destination Location to On this System.
To set up a push remote replication in the replication wizard, set the Source Location to On this System and set Destination Location to On a Different System. To set up a pull remote replication in the replication wizard, set the Source location to On a Different System and the Destination Location to On this System.
Setting either source or destination to On a Different System automatically sets the other to On This System. You cannot set both to On a Different System.
Click on Source Location or Destination Location to show additional setting options and the file browser. Additional settings shown are based on the selection.
Configure the settings for remote replication after selecting On a Different System in either Source Location or Destination Location.
a. Select an existing SSH connection from the dropdown list or select Add New to open the New SSH Connection screen. If you created the SSH connection in the section above, select it.
When adding a new connection in the wizard, if TrueNAS detects other configuration issues, such as the user not correctly set up, an error indicating what the issue is shows in the wizard. Exit the replication wizard to correct issues, then return to the wizard to begin the task configuration again.
After completing the replication wizard task creation, where you added a new SSH connection in the wizard, return to the remote system user configuration to add the new public key for the SSH connection to the admin user configuration.
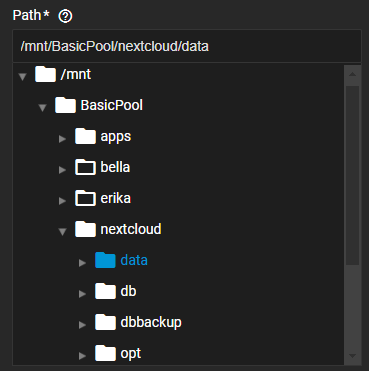
b. Use the file browser to browse and select the parent dataset with the data to replicate. Clicking on the dataset(s) populates the path.
When setting up the Source, you can select multiple sources or manually type the names into the Source field.
When setting up the Destination, the Destination path allows adding a directory/dataset by entering /name, where rname is the name of a directory or dataset. The source path does not allow adding a new dataset/directory. You cannot use zvols as a remote replication destination. Add a name to the end of the path to create a new dataset in that location.
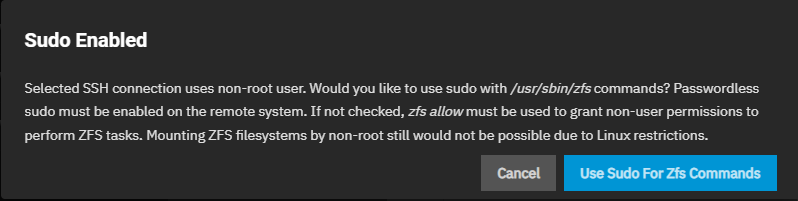
c. Select Use Sudo for ZFS Commands. A dialog opens prompting you to add this capability. Selecting this removes the need to issue the cli
zfs allowcommand in Shell on the remote system. Click Use Sudo for ZFS Commands. If the dialog closes before clicking this option, you can select this option on the wizard screen.d. Enter the settings for the other location (source or destination), which is automatically set to On This System. Browse to select the dataset.
e. (Optional) Select Encryption to add a second layer of encryption over the already encrypted dataset.
(Optional) Select Replicate Custom Snapshots, then leave the default value in Naming Schema. If you know how and want to enter the schema, enter it in Naming Schema.
A snapshot naming schema identifies the snapshots to replicate, and might be required by the remote system. A naming schema is a string of strftime(3) %Y, %m, %d, %H, and %M variables that name custom snapshots you want to replicate. Separate entries by pressing Enter. The number of snapshots matching the pattern entered shows on a dropdown list.
Selecting Matching regular expression does not automatically destroy snapshots, whereas selecting Matching naming schema does. When using a regular expression, the snapshots on the destination host are not automatically destroyed when they are destroyed on the source host due to the snapshot lifetime. Snapshots on the destination host display as “Will not be destroyed automatically” and do not display with a retention period. Use naming schema for these.
(Optional) Select Recursive to replicate all snapshots contained within the parent dataset and any child datasets.
(Optional) Accept the default name in Task Name, or enter a name of your choosing. TrueNAS populates this field with a default name using the source and destination paths separated by a hyphen, but this default can make locating the snapshot in the destination dataset a challenge. To make it easier to find the snapshot, give it a name that is easy to identify. For example, a replicated task named dailyfull for a full file system snapshot taken daily.
Click Next to show the scheduling options.
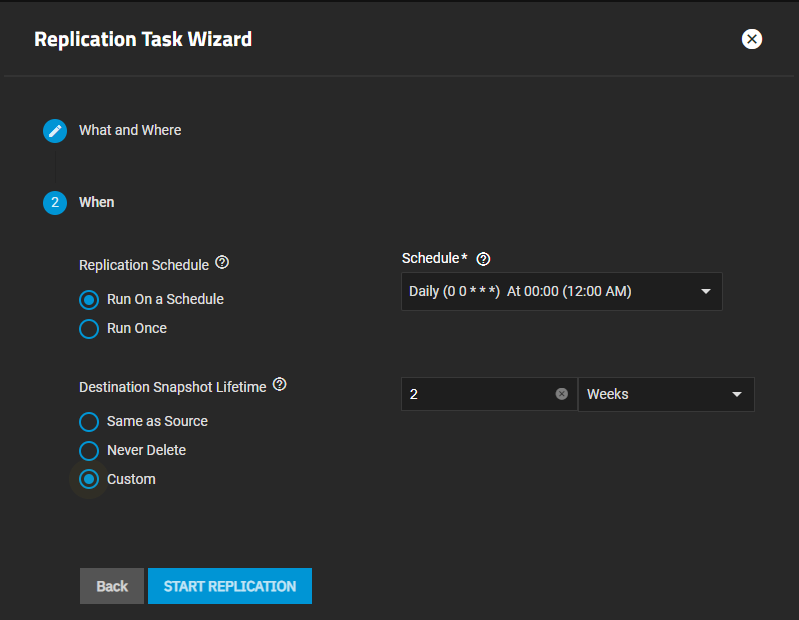
Select the schedule and snapshot retention lifetime.
LeaveReplication Schedule set to Run On a Schedule and select the option in the Schedule dropdown. Select Run Once to set up a replication task you run one time.
Select the Destination Snapshot Lifetime option to specify how long TrueNAS should store copied snapshots in the destination dataset before TrueNAS deletes it. Same as Source is selected by default. Select Never Delete to keep all snapshots until you delete them manually. Select Custom to show two additional settings, then enter the number of the duration you select from the dropdown list. For example, 2 Weeks.
Click Save.
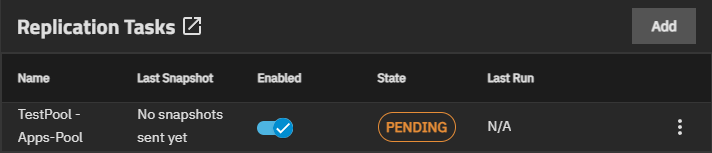
The task shows on the Replication Task widget with the status as PENDING.
Select Run Now if you want to run the task immediately.
Click the task State to open a dialog with the log for that replication task.
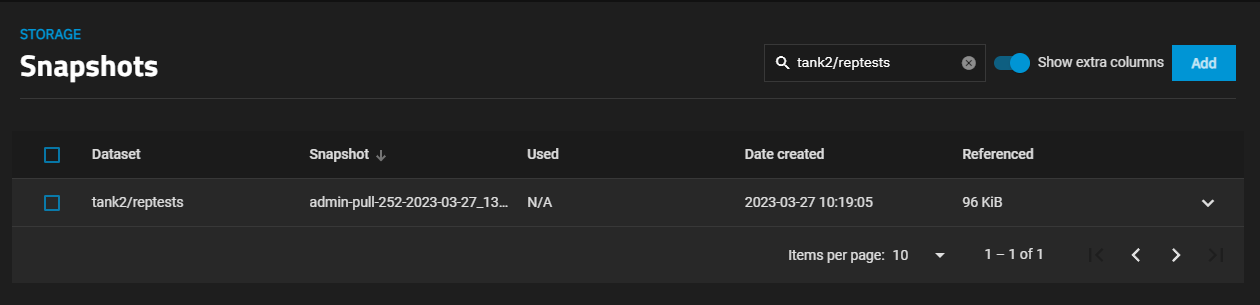
To see the replication snapshots, go to Datasets, select the destination dataset on the tree table, then select Manage Snapshots on the Data Protection widget to see the list of snapshots in that dataset. Click Show extra columns to add more information columns to the table, such as the date created, which can help you locate a specific snapshot or enter part of or the full name in the search field to narrow the list of snapshots.
For information on replicating encrypted pools or datasets, see Setting Up an Encrypted Replication Task.
When using a TrueNAS system on a different release, the remote or destination system user is always root.
To configure a new SSH connection while in the Replication Task Wizard:
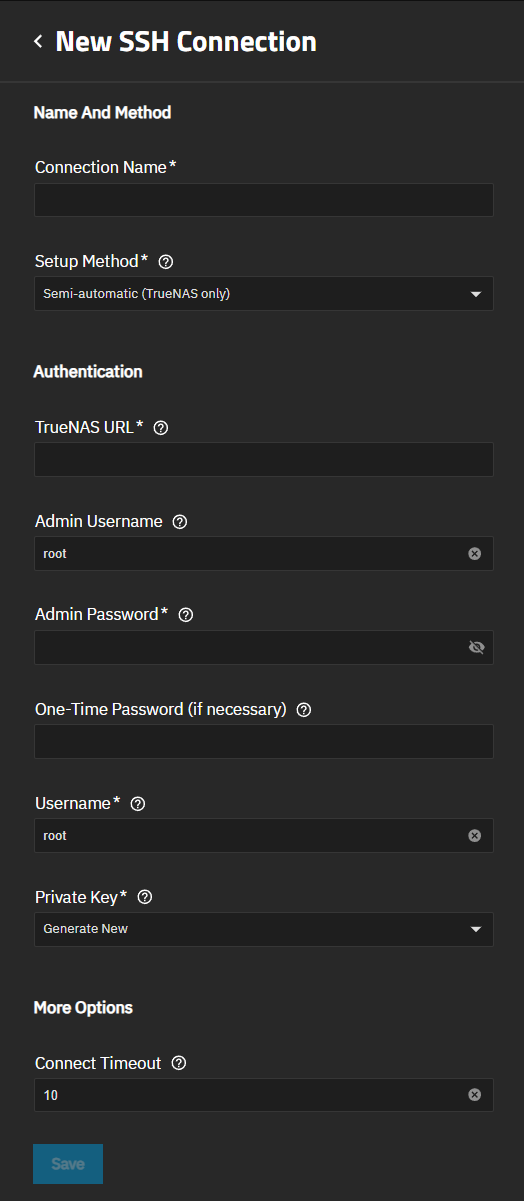
Select Add New on the SSH Connection dropdown list to open the New SSH Connection screen.
Enter a name for the connection.
Select the Setup Method from the dropdown list. Leave this set to Semi-Automatic for a connection to another TrueNAS system.
Enter the remote TrueNAS host name or IP address as a URL in TrueNAS URL.
Enter the administration user (i.e., root or admin) that logs into the remote system with the web UI in Admin Username. Enter the password in Admin Password.
If using a TrueNAS 13.0-U6.x system as the remote server, the remote user is always root.
When using an earlier TrueNAS 22.12.1 system or if you installed TrueNAS as the root user and then created an admin user after initial installation, you must verify that the admin user is correctly configured.
Enter the administration user (i.e., root or admin) for the remote system SSH session. If you clear root as the the user and type any other name the Enable passwordless sudo for ZFS commands option displays. This option does nothing, so leave it cleared.
Select Generate New from the Private Key dropdown list.
(Optional) Enter a new value in seconds for the Connection Timeout if you want to change the defaults.
Click Save to create a new SSH connection and populate the SSH Connection field in the Replication Task Wizard.
After creating a new SSH connection, go to Credentials > Backup Credentials > SSH Connections, click Edit to copy the public key, then edit the remote user configuration by pasting this in the Public SSH Key field.
We always recommend using encryption for SSH transfer security.
In situations where you use two systems within an absolutely secure network for replication, disabling encryption speeds up the transfer. However, the data is completely unprotected from eavesdropping.
Choosing No Encryption for the task is less secure but faster. This method uses common port settings but you can override these when using the Advanced Replication Creation options or by editing the task after creating it in the wizard.