TrueNAS CORE Nightly Development Documentation
This content follows experimental early release software. Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to a stable software release.
Creating Certificate Authorities (CAs)
4 minute read.
Last Modified 2023-11-30 10:15 ESTTrueNAS can act as a certificate authority (CA). When encrypting SSL or TLS connections to the TrueNAS system, you can import an existing CA or create a CA and certificate on the TrueNAS system. The certificate appears on the dropdown menus for services that support SSL or TLS.
Go to System > CAs and click ADD. Enter a name for the CA, then choose the type from the Type dropdown list of three, Internal CA, Intermediate CA, or Import CA. The process to add a CA for each type is slightly different.
A CA must exist in CORE to add an Intermediate CA. This can be an internal or imported CA.
To create a CA:
Enter or select the Identifier and Type setting options.
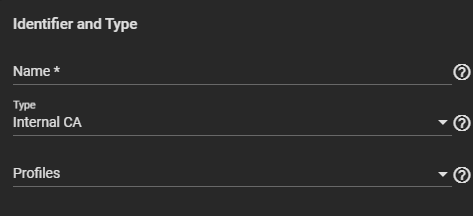
a. Enter a name for this CA. b. Select Internal CA from the Type dropdown list to create an internal certificate. Select Intermediate CA to create an intermediate certificate. This displays the Signing Certificate Authority field in Certificate Options.
Select an option from the Profiles dropdown list. A profile for the CA auto-fills options like Key Type, Key Length, and Digest Algorithm. Otherwise, you must set options manually.
To add an OpenVPN Root CA, select OpenVPN Root CA. The configuration form populates with default settings, enables Basic Constraints, Authority Key Identifier, Extended Key Usage, and Key Usage, and sets the options for each extension.
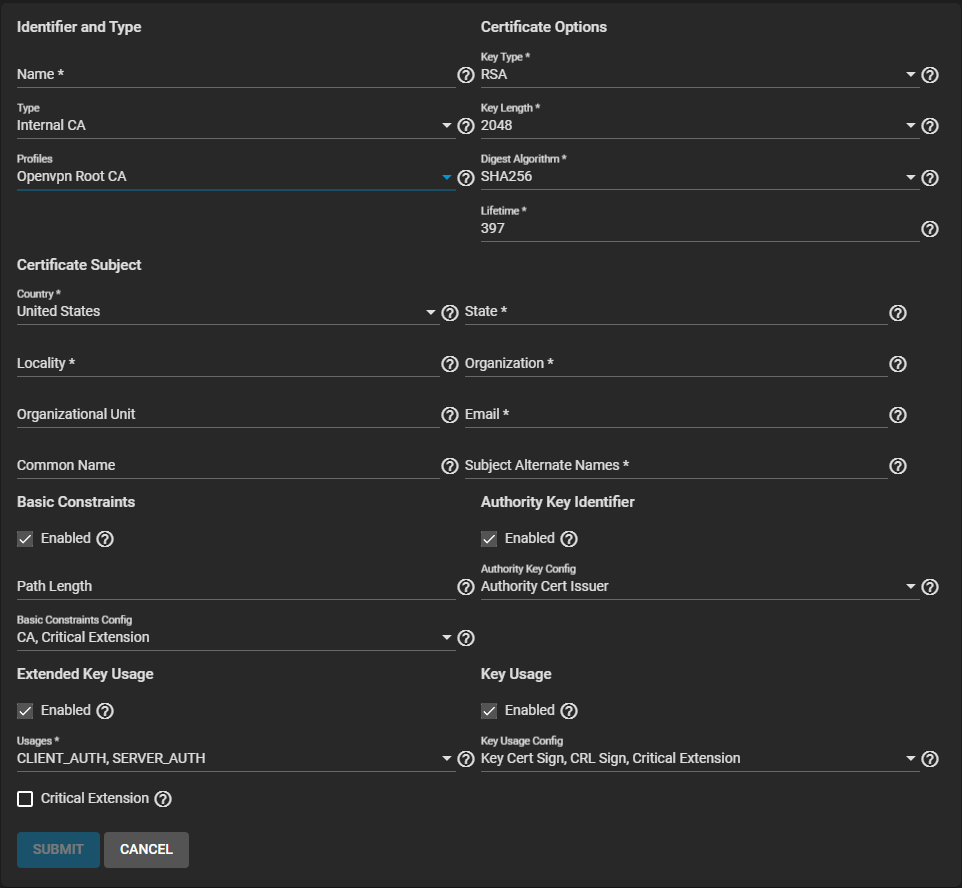
To add CA certificate, select CA. The configuration form populates with default settings, enables Basic Constraints, Authority Key Identifier, Extended Key Usage, and Key Usage, and sets the options for each extension.

Select the Certificate Options.
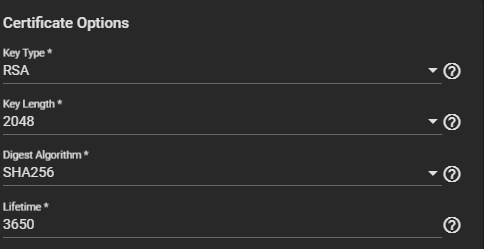
a. Select a Key Type from the dropdown list. We recommend the RSA key type. Use EC for elliptic curve certificates.
b. Select the Key Length. We recommend a minimum of 2048 for security reasons.
c. Select a Digest Algorithm. We recommend SHA256.
d. Enter the Lifetime of the CA in days to set how long the CA remains valid.
Enter or select the Certificate Subject settings.
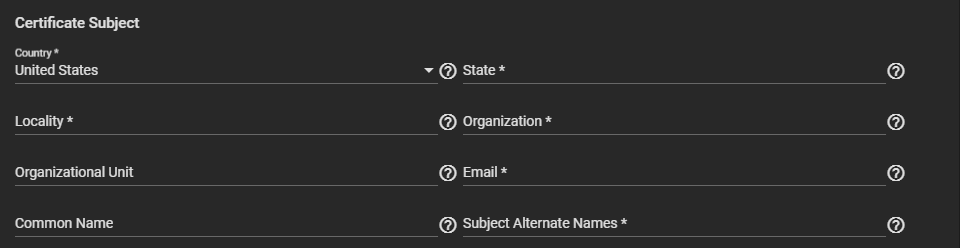
a. Enter the geographic information in Country, Locality, Organizational Unit (optional), Common Name, State, Organization, Email, and Subject Alternate Names.
b. (Optional) Enter a fully-qualified hostname (FQDN) that is unique within a certificate chain in Common Name.
Select enable and select extensions to use if you did not select an option in Profiles. If manually selecting and entering extension:
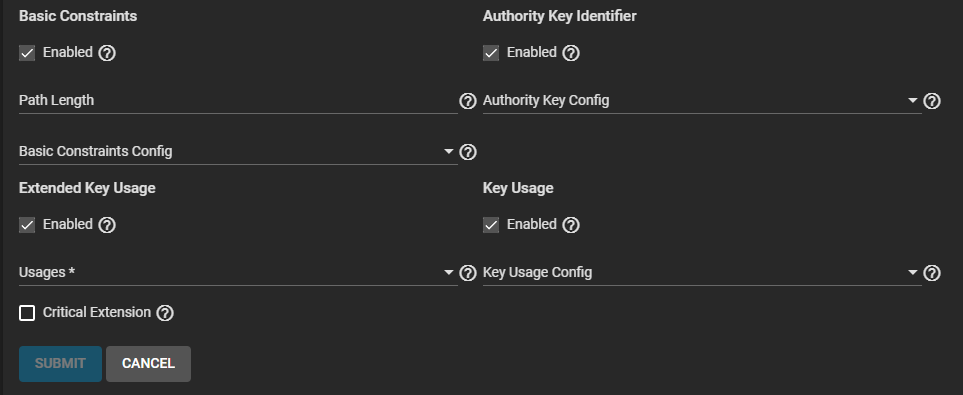
a. Select Enable, then enter the extensions for Basic Constraints.
Enter a value in Path Length that determines how many non-self-issued intermediate certificates can follow the certificate in a valid certification path. Entering 0 allows a single additional certificate to follow in the certificate path. Then select the extension(s) to use.
Select an option from the Basic Constraints Config dropdown list. Select CA to use a certificate authority. Selecting Critical Extension can result in rejection of the certificate by the system that is using the certificate if that system does not recognize the extension.
b. Select Enable, then enter the extensions for Authority Key Identifier.
Enabling Authority Key Config adds the authority key identifier extension which provides a means of identifying the public key corresponding to the private key used to sign the certificate. Used when an issue has multiple signing keys, possibly due to multiple concurrent key pairs or due to changeover. Options are Authority Cert Issuer or Critical Extension.
c. Select Enable, then enter the extensions for Extended Key Usage. Select one or more usages for the public key from the Usages dropdown list. TrueNAS uses Extended Key Usage for end-entity certificates.
Enable Critical Extension to identify this extension as critical for the certificate. Do not enable Critical Extension if Usages contains ANY_EXTENDED_KEY_USAGE.
Using Extended Key Usage and Key Usage extensions requires that the certificate purpose is consistent with both extensions. See RFC 3280, section 4.2.1.13 for more details.
Click Submit to create the CA.
Use this procedure to import a CA.
Enter a name for this certificate.
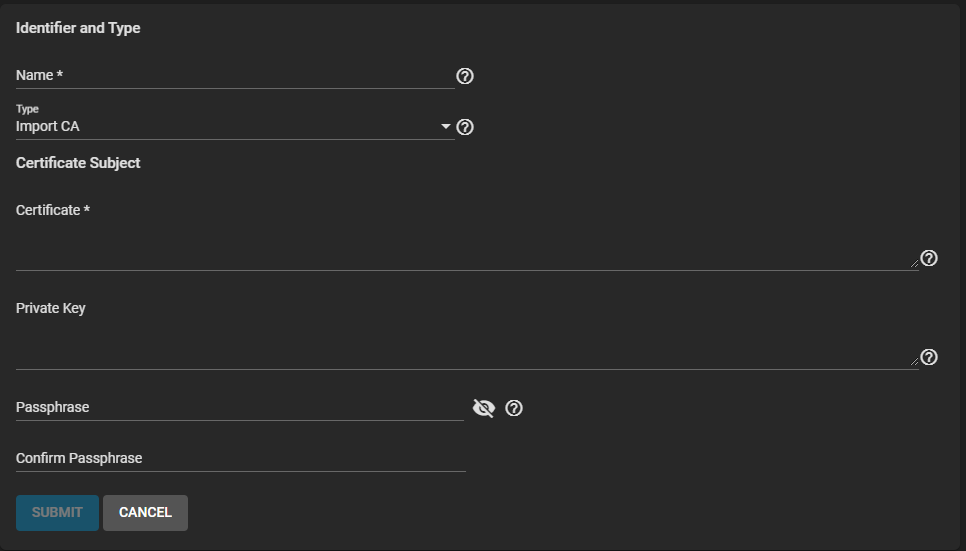
Select Import CA from the Type dropdown list.
Copy the certificate for the CA you want to import and paste it into the Certificate field.
Paste the certificate private key of at least 1024 bits in length into Private Key when available.
Enter and confirm the passphrase for the private key into Passphrase and Confirm Passphrase.
Click Submit.
Before deleting a CA, verify it is not used by another service such as S3, FTP, etc. You cannot delete a CA when in use by other services.
Also, before you can delete a CA, you need to delete certificates issued by the CA or those relying on the CA. If you receive an error that mentions foreign keys reference, ensure the certificates on your system do not use the CA you want to delete.

