TrueNAS CORE Nightly Development Documentation
This content follows experimental early release software. Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to a stable software release.
Setting Up a Network VLAN
2 minute read.
Last Modified 2024-03-15 13:07 EDTA virtual LAN (VLAN) is a specialized domain in a computer network. It is a domain partitioned and isolated at the data link layer (OSI layer 2). See here for more information on VLANs. TrueNAS uses vlan(4) to manage VLANS.
To set up a VLAN interface, go to Network > Interface > Add.
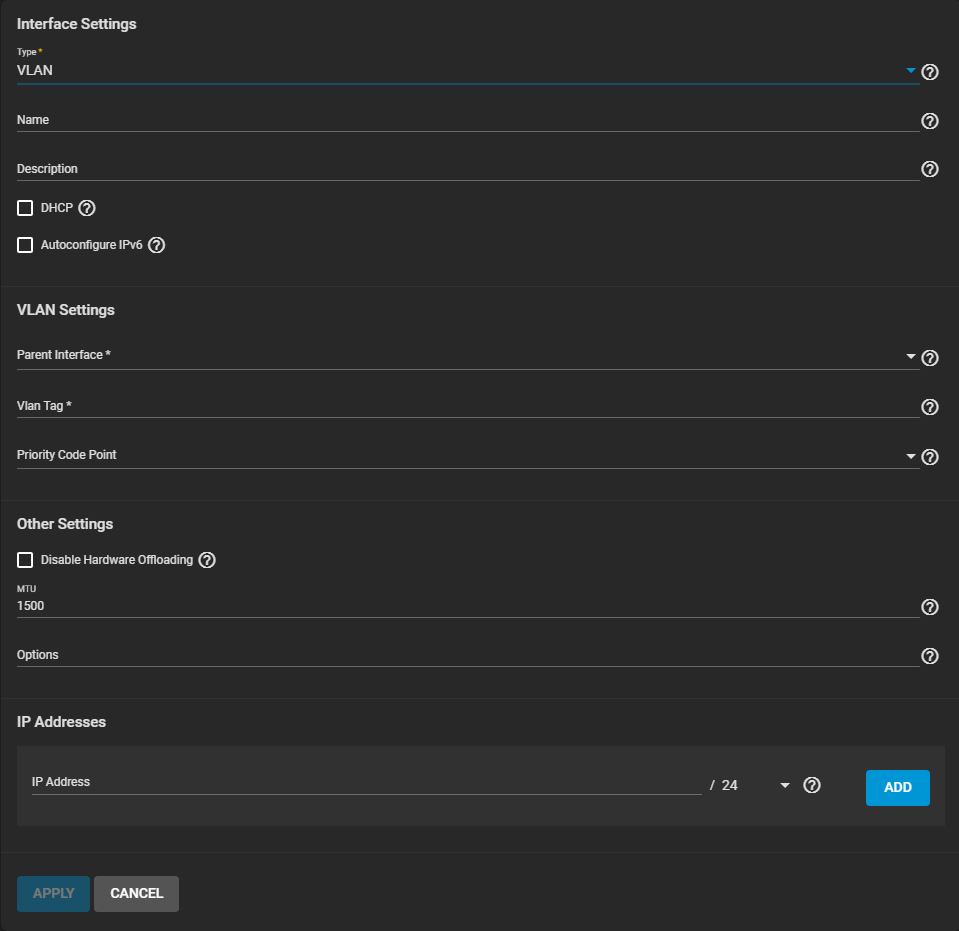
Set the Type to VLAN and enter a name for the interface in Name. The name must use the format vlanX, where X is a number representing a non-parent interface. Enter any notes or reminders about this VLAN in the Description field.
Determine the requirements of your network environment before enabling DHCP or AutoconfigureIPv6. It is important to understand how this new interface functions in your situation. By default, TrueNAS allows only one network interface to have DHCP enabled.
Give careful attention to the remaining VLAN Settings. These need proper configuration in order for the network interface to function.
- Parent Interface where you select the VLAN parent interface. This is usually an Ethernet card connected to a switch port already configured for the VLAN.
- Vlan Tag where you enter a numeric tag for this interface. This is usually preconfigured in the switched network.
- Priority Code Point where you define the VLAN Class of Service.
There are a few extra interface options to review after the VLAN options are set.
See Interfaces Screen for more information on settings.
Every kind of network interface has common settings:
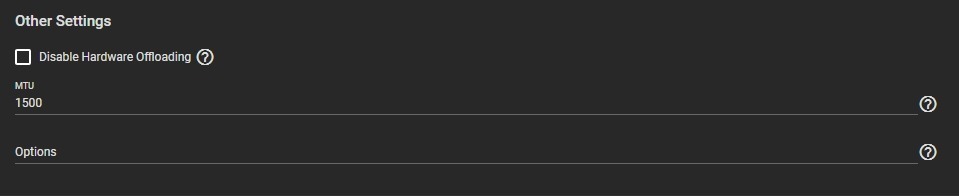
Disabling Hardware Offloading can reduce network performance. It is not recommended.
Disabling this option is sometimes necessary. For example, when the interface is managing jails, plugins, or virtual machines.
MTU stands for maximum transmission unit. It is the largest protocol unit for transferring data. MTU size varies. Physical hardware and available network interfaces determine the largest workable MTU size. 1500 and 9000 are standard Ethernet MTU sizes. The recommendation is to use the default 1500. The permissible range of MTU values is 1492-9216. Leaving this field blank sets the default value of 1500.
You can enter more tuning ifconfig settings in the Options.
Additional aliases for the interface can also be defined:
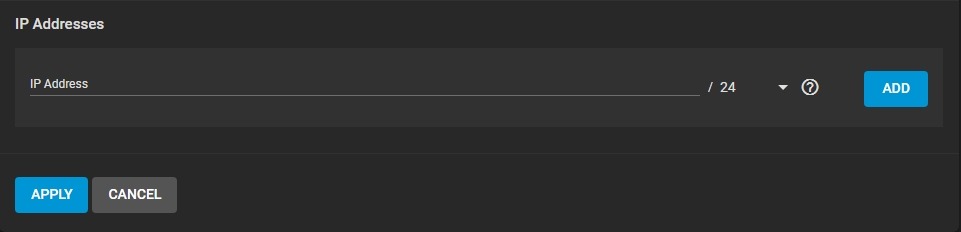
It is possible to define either IPv4 or IPv6 addresses and subnets from 1-32. Clicking Add provides another field for defining an IP address.

