TrueNAS CORE Nightly Development Documentation
This content follows experimental early release software. Use the Product and Version selectors above to view content specific to a stable software release.
Jails
10 minute read.
Last Modified 2024-05-17 15:03 EDTAs of TrueNAS CORE 13.3, this feature is untested and provided without support to the TrueNAS Community.
Users with a critical need to use containers or virtualization solutions in production should migrate to the tested and supported virtualization features available in TrueNAS SCALE. TrueNAS Enterprise customers can contact iXsystems to schedule a TrueNAS SCALE deployment. See CORE to SCALE Migrations for more information.
Jails are a lightweight, operating-system-level virtualization. One or multiple services can run in a jail, isolating those services from the host TrueNAS system. The main differences between a user-created jail and a plugin are that plugins are preconfigured and usually provide only a single service.
It is important to understand that users, groups, installed software, and configurations within a jail are isolated from both the TrueNAS host operating system and any other jails running on that system.
The ability to create multiple jails offers flexibility regarding software management. For example, an administrator can choose to provide application separation by installing different applications in each jail, to create one jail for all installed applications, or to mix and match how software is installed into each jail.
You must create a data storage pool before using jails. Make sure the pool has enough storage for all of the intended jails. The Jails screen displays a message and the CREATE POOL button if a pool does not exist on the TrueNAS system.
If pools exist, but one is not chosen to use with jails or plugins, a dialog displays prompting you to choose a pool. Select a pool and click CHOOSE.
To select a different pool for jail and plugin storage, click the settings icon, then select a different pool from the dropdown list.
TrueNAS uses iocage for jail and plugin management. Jails and downloaded FreeBSD release files are stored in a dataset named iocage.
See Setting Up Jail Storage for more information on jail storage and mount points.
TrueNAS has two options to create a jail, the jail Wizard or ADVANCED JAIL CREATION. The jail Wizard provides the simplest process to create and configure a new jail. The ADVANCED JAIL CREATION alternate method has every possible configurable jail option. See [Jails Screen](/core/uireference/jailspluginsvms/jailsscreens/ for more information on jails screens and configuration settings.
To add a new jail, go to Jails then click ADD. The Wizard opens. To access the advanced configuration option, click ADVANCED JAIL CREATION at the bottom of the Wizard screen. We recommend only advanced users with very specific use applications use this method to create a jail.
Enter a name for the jail. Names can contain letters, numbers, periods (.), dashes (-), and underscores (_).
Select the jail type. Default (Clone Jail) or Basejail. Clone jails are clones of the specified FreeBSD release. They are linked to that release, even if they are upgraded. Basejails mount the specified release directories as nullfs mounts over the jail directories. Basejails are not linked to the original release when upgraded.
Specify the release to use. Options are 12.4-RELEASE or 13.2-RELEASE. Jails can run FreeBSD versions up to the same version as the host TrueNAS system. Newer releases are not shown. Versions of FreeBSD are downloaded the first time they are used in a jail. Additional jails created with the same version of FreeBSD are created faster because the download is already completed.
Click Next to display the Configure Networking wizard screen with a simplified list of networking options.
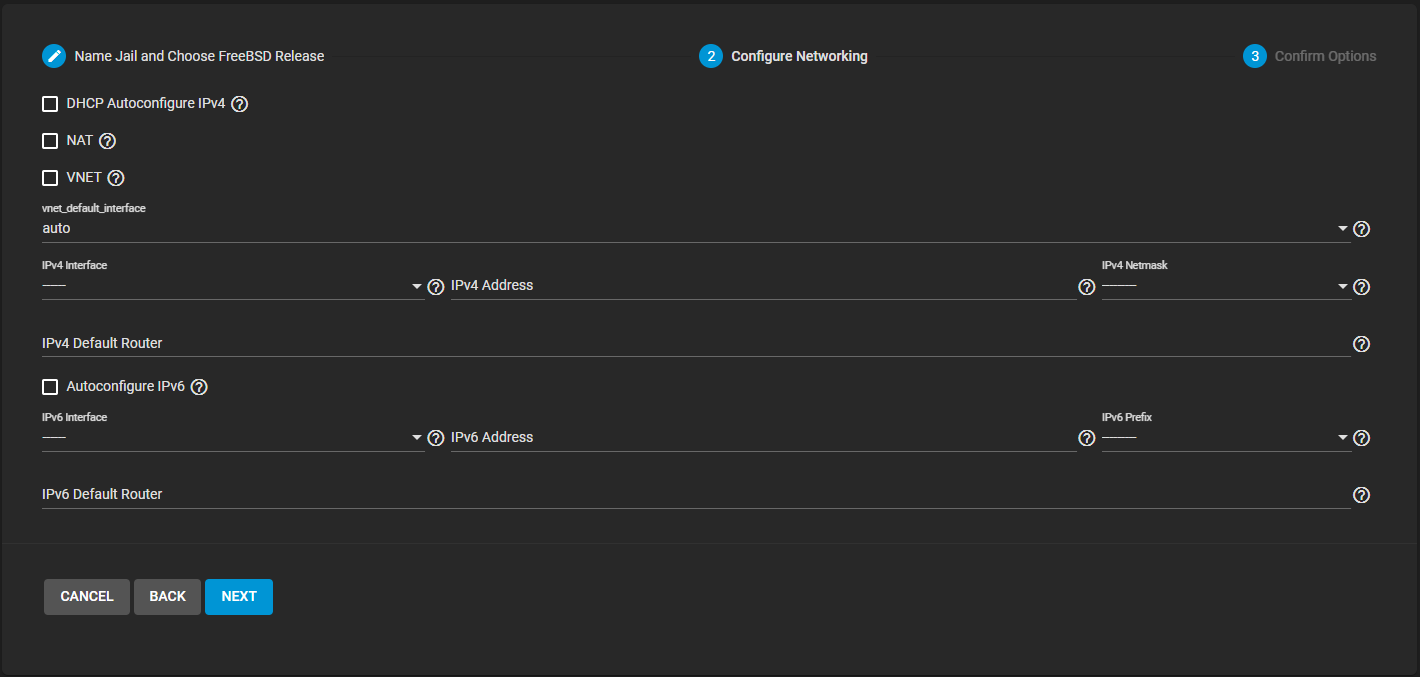
Click NEXT to view a summary of the chosen jail options. Click SUBMIT to create the new jail. After a few moments, the new jail is added to the Jails screen list.
From the Jails screen click on ADD to open the Wizard, then click on ADVANCED JAIL CREATION at the bottom of the screen to open the Advanced Jail Creation form.
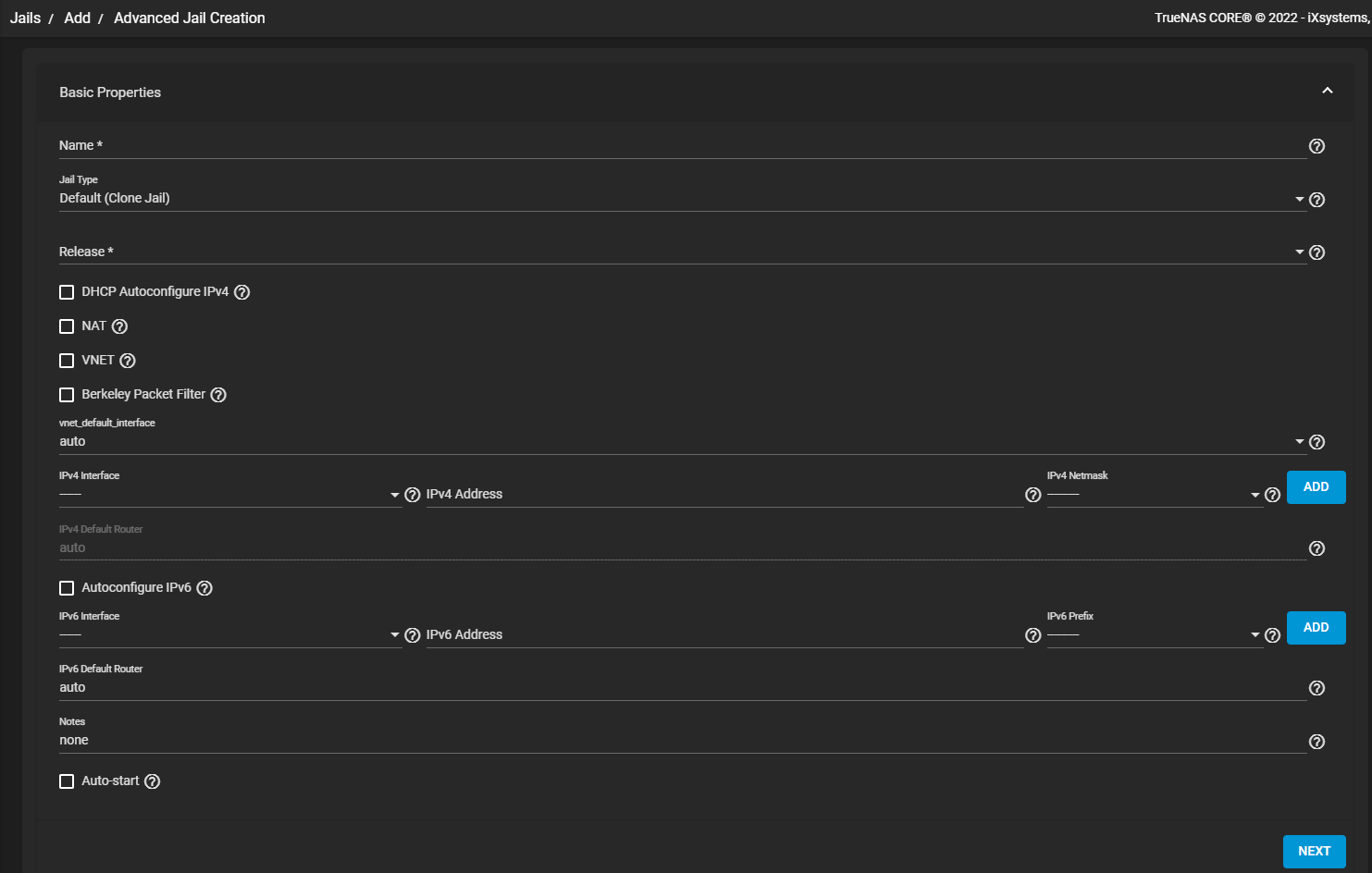
Enter the jail name, type, and select the release just as in the Name Jail and Choose FreeBSD Release Wizard screen.
Enter the networking settings leave all blank to create the jail without networking.
Click on Jail Properties to enter the settings for a jail ruleset to follow, commands to run in the system or jail environment, add a jail user, set allow or deny SYSV IPC message, shared memory, or semaphore primitives. You can also add VNET interfaces and other jail settings on this screen.
Click on Network Properties to add interfaces, host names, domain names, and resolver addresses, disable IPv4 or IPv6 source address selection for the jail in favor of the primary IPv4 or IPv6 address of the jail (only available when the jail is not configured to use VNET). You can also set the IPv4 or IPv6 IP address to inherit or restrict access to all system addresses or stop the jail from using either IPv4 or IPv6 entirely. You can configure MAC address settings.
Click Custom Properties to add the priority for the jail at boot time, jail host ID, set up the jail as a template. You can add system host time to synchronize time between the jail and host, enabling ZFS jailing inside the jail, define a dataset to be jailed and to be fully handed over to a jail, enter a mount point for the jail_zfs_dataset, configure tun settings, and add other local host, IP host name, and IPV6 autoconfigure settings.
Click SAVE to add the jail and return to the Jails screen.
You can create a usable jail without any networking by entering only the required Jail Name, selecting the Jail Type, and Release. To create a jail without networking, leave all network checkboxes cleared and fields empty to initialize the jail without any networking abilities.
To add networking to the jail after creation, go to Jails, click the chevron_right for the jail, then click edit Edit. Configure the network settings in the Basic Properties area when the jail needs to communicate over the local network or out to the internet.
If you are an experienced user you can access additional advanced configuration settings in the Network Properties, and Custom Properties sections.
For more information on the configuration screens, see Jails Screens.
A template jail is a jail using the basejails type and customized with other software that can efficiently create other jails with the same configuration.
To create a template jail go to Jails, click ADD then click ADVANCED JAIL CREATION at the bottom of the Wizard screen, then:
Create a jail to use as a template.
a. Enter a name for the jail template, select Basejail as the Jail Type, and select the release from the Release dropdown.
b. Configure the other jail setting you want to save in the template.
c. Click SAVE to create the template and add this jail to the
iocage/templates folder and list of available releases.Start this new jail, then click Shell to install the custom software packages. See Installing Jail Software for more information on customizing your jail template.
Click SAVE.
Click Stop to stop the jail.
Click Edit to open the Edit Advanced Jail Creation screen and make the jail a template.
a. Click on Custom Properties to show that section, then select Template.
b. Click Save.
The new template jail shows on the Releases dropdown list.
Add a new jail from the template.
a. Click ADD to open the Wizard.
b. Enter a name, select Default (Clone Jail), then select the name of the template from the Releases dropdown list.
c. Click NEXT to enter networking settings.
d. Click NEXT to review your settings and if satisfied with the settings, click SUBMIT to add the jail.
You can select the Advanced Jail Creation option if you want to enter any other advanced settings not included in the template.
You must use the ADVANCED JAIL CREATION screens to create the basejail you want to use as a template. If you use the Wizard to create the basejail, then edit it to make it a template, any new jails created from this template do not start.

